Introduction
In 2025, the business landscape is increasingly complex, and so are the risks associated with vehicle operations. With evolving regulations, technological advancements, and emerging risks such as cyber threats linked to connected vehicles, it is more important than ever to ensure your business auto insurance policy fits your unique needs.
This article explores the types of commercial auto insurance, the coverage options available, factors to consider when selecting a policy, and how to ensure your business is adequately protected.
Key Takeaways
- Business auto insurance is different and more comprehensive than personal auto insurance, designed for commercial use vehicles.
- Essential coverages include liability, physical damage, medical payments, and hired/non-owned auto protection.
- Properly assessing your fleet size, business risks, and regulatory requirements is crucial to selecting the right policy.
- Technology such as telematics can enhance safety and reduce premiums.
- Regular policy reviews and updates ensure continuous, adequate coverage as your business grows.
Understanding Business Auto Insurance
Business auto insurance is a specialized type of insurance coverage designed to protect vehicles used primarily for business purposes. Unlike personal auto insurance, which covers private use vehicles, business auto insurance accounts for the unique risks and liabilities associated with operating vehicles as part of a commercial enterprise.
Why Business Auto Insurance Is Different
When a vehicle is used in the course of business—whether for transporting goods, delivering services, or traveling between job sites—it faces a different risk profile than a personal vehicle used solely for commuting or leisure. These risks include:
- Increased mileage and time on the road: Business vehicles typically cover more miles daily, increasing the likelihood of accidents.
- Multiple drivers: Business vehicles might be operated by several employees, adding complexity to liability and risk.
- Higher liability exposure: Accidents involving business vehicles may result in larger claims, including injury to third parties or damage to commercial property.
- Cargo risks: Vehicles that transport goods or equipment might require additional protection for the items being carried.
Because of these factors, business auto insurance policies offer broader coverage and higher liability limits tailored to commercial needs, which personal policies usually exclude or limit.
Types of Vehicles Covered by Business Auto Insurance
Business auto insurance policies are flexible and can cover a variety of vehicle types depending on the needs of the business:
- Company Cars: Standard passenger vehicles owned or leased by the company and used by employees for business-related travel.
- Delivery Vans and Trucks: Vehicles specifically used for transporting products or materials to customers or job sites. This category includes light-duty vans and medium-duty trucks.
- Commercial Fleets: Larger businesses may have a fleet of vehicles, ranging from sedans to heavy trucks, all insured under a single business auto policy.
- Specialty Vehicles: Certain industries require coverage for specialized vehicles such as tow trucks, construction machinery, dump trucks, or refrigerated trucks. These vehicles often need customized coverage options due to their specific functions and associated risks.
Why Personal Auto Insurance Isn’t Enough for Business Vehicles
Many business owners may mistakenly believe that their personal auto insurance covers their business vehicles. However, this is rarely the case because personal auto policies typically include explicit exclusions for vehicles used for commercial purposes.
Here’s why relying solely on personal auto insurance is risky:
- Claim Denials: If an accident occurs while the vehicle is being used for business purposes, the insurer may deny the claim because the policy excludes commercial use.
- Legal Exposure: Without proper commercial coverage, your business could be liable for damages out-of-pocket, including property damage, medical expenses, and legal fees.
- Financial Loss: Lack of adequate coverage can result in substantial financial losses if your business vehicle is involved in an accident or theft.
- Regulatory Non-Compliance: Many states and industries mandate specific commercial auto insurance requirements that personal policies do not satisfy, potentially resulting in fines or legal action.
Essential Coverages in Business Auto Insurance
Liability Coverage

Liability coverage is the cornerstone of any business auto insurance policy. It protects your business if your vehicle causes injury or damage to others, including third-party individuals and their property. This coverage is legally required in most states and typically includes two major parts:
- Bodily Injury Liability:
This coverage pays for medical expenses, rehabilitation costs, lost wages, and legal fees if your business vehicle causes injuries to other people in an accident. For example, if your delivery van is involved in a crash that injures a pedestrian or another driver, bodily injury liability helps cover their medical bills and any legal settlements or judgments. - Property Damage Liability:
This pays for the repair or replacement of someone else’s property damaged by your business vehicle. This could include damage to other vehicles, buildings, fences, or infrastructure caused by a collision or accident involving your company vehicle.
Why it matters:
Without adequate liability coverage, your business could face significant out-of-pocket expenses or lawsuits, which could threaten your financial stability.
Physical Damage Coverage
Physical damage coverage protects your business’s vehicles from damage resulting from accidents or other perils. It usually consists of two parts:
- Collision Coverage:
Covers damage to your vehicle resulting from collisions with other vehicles, objects (like trees or poles), or due to rollover accidents. If your company truck hits another vehicle or crashes into a barrier, collision coverage pays for repairs or replacement. - Comprehensive Coverage:
Covers damage to your vehicle caused by events other than collisions, such as theft, fire, vandalism, natural disasters (like floods, hail, or earthquakes), or hitting an animal. For example, if your business vehicle is stolen or damaged by a storm, comprehensive coverage reimburses the cost of repairs or replacement.
Importance:
Physical damage coverage is optional but highly recommended, especially for newer or more valuable business vehicles. It ensures that your business doesn’t bear the full financial burden of repairing or replacing damaged vehicles.
Medical Payments Coverage
Medical payments coverage (often called MedPay) pays for medical expenses incurred by the driver and passengers of your business vehicle following an accident, regardless of who is at fault. This coverage can include hospital bills, doctor visits, surgery, and rehabilitation.
Why it’s useful:
This coverage helps cover immediate medical costs without the need to determine liability first, speeding up access to care for employees or clients in your vehicles.
Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage
This coverage protects your business if your vehicle is involved in an accident with a driver who either has no insurance (uninsured motorist) or insufficient coverage (underinsured motorist) to pay for the damages they cause.
Why this matters:
Many drivers operate vehicles without adequate insurance, and without this coverage, your business could be left paying for costly repairs or medical bills resulting from an accident with such a driver.
Hired and Non-Owned Auto Coverage
This coverage is crucial for businesses that use vehicles they don’t own but rely on for operations. It protects your company in two key scenarios:
- Hired Auto Coverage:
Covers vehicles your business rents, leases, or borrows. For example, if your company rents a van for a delivery job, hired auto coverage provides liability and physical damage protection for that vehicle during the rental period. - Non-Owned Auto Coverage:
Protects your business when employees use their personal vehicles for work purposes. For example, if an employee uses their own car to visit clients or make deliveries and gets into an accident, this coverage helps cover liability and damages related to the business use of that vehicle.
Why you need it:
Many businesses rely on vehicles they do not own, and without this coverage, the business could be exposed to significant liability risks if an accident occurs while using rented or employee-owned vehicles for work.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Business Auto Insurance
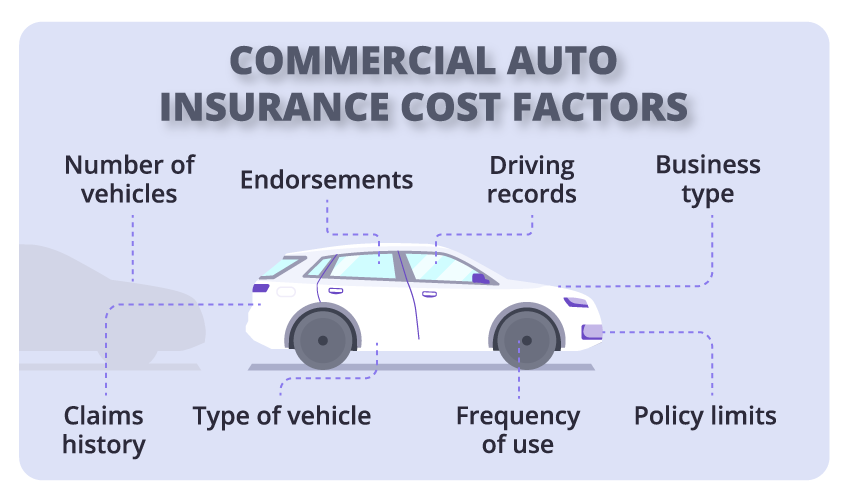
Selecting the right business auto insurance policy is a crucial step in protecting your company’s assets, employees, and overall financial health. However, because businesses vary widely in size, operations, and risk exposure, the “best” policy will depend on several important factors. Below, we explore these considerations in detail to help you make an informed decision.
Size and Type of Your Fleet
One of the first things insurers consider is the composition and scale of your fleet. This directly influences your coverage needs and premium costs.
- Number of Vehicles:
A larger fleet typically requires a comprehensive policy that covers all vehicles efficiently. Insurers may offer fleet discounts or specialized commercial policies for multiple vehicles, which can help reduce costs. - Types of Vehicles:
The kinds of vehicles you operate matter. For instance, passenger cars, delivery vans, heavy-duty trucks, or specialty vehicles (like refrigerated trucks or tow trucks) carry different risks and coverage needs. Commercial trucks might require higher liability limits and additional endorsements compared to standard company cars. - Usage Patterns:
How you use your vehicles impacts risk exposure. Vehicles used for local deliveries with short routes have different risk profiles than those used for long-haul freight across states. Long-distance operations may face more exposure to accidents, weather-related risks, and regulatory scrutiny.
Understanding these details helps insurers tailor a policy that reflects your actual risk, avoiding both under-coverage and unnecessary costs.
Business Risks and Exposure
Different industries face distinct risks related to vehicle operation, which must be factored into your insurance coverage:
- Industry-Specific Risks:
Businesses in construction, logistics, food delivery, or passenger transport encounter unique challenges. For example, construction vehicles may operate in hazardous environments with heavy machinery, increasing the risk of accidents and property damage. Food delivery services face risks associated with time-sensitive routes and potential for distracted driving. - Frequency and Nature of Vehicle Use:
How often and for what purpose vehicles are used also affects risk. Vehicles constantly on the road with heavy usage cycles will have higher exposure than those used occasionally for business errands. - Locations of Operation:
Urban vs. rural operations present different challenges. Urban areas might have higher traffic density, increasing accident risk, while rural areas may face hazards such as poor road conditions or wildlife. Additionally, some regions are more prone to natural disasters, theft, or vandalism, influencing coverage needs and premiums.
Evaluating these factors allows your insurer to provide policies that adequately reflect your business’s unique operational hazards.
Regulatory Requirements
Compliance with local, state, and industry-specific regulations is mandatory for businesses operating commercial vehicles. Understanding these requirements is vital when choosing your business auto insurance:
- State Minimum Insurance Requirements:
Each state mandates minimum liability coverage limits for commercial vehicles, which may differ from personal auto insurance minimums. Insurers must ensure that your policy meets or exceeds these legal requirements. - Industry-Specific Regulations:
Certain industries, such as trucking or passenger transport, must comply with federal regulations enforced by entities like the Department of Transportation (DOT). These often require higher liability limits, specific coverage types, or regular audits.
Failure to comply can result in fines, penalties, or even suspension of business operations, making regulatory adherence a top priority when selecting insurance.
Budget and Premium Costs
While adequate coverage is essential, your business must also balance protection with cost efficiency:
- Balancing Coverage Limits and Deductibles:
Higher coverage limits provide better protection but result in higher premiums. Conversely, choosing higher deductibles can lower premiums but increases out-of-pocket costs when filing claims. A careful balance must be struck based on your business’s risk tolerance and financial capacity. - Potential Discounts:
Many insurers offer discounts for safety features such as GPS tracking, anti-theft devices, or advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Additionally, driver training programs, safe driving records, and fleet safety policies can qualify your business for reduced premiums. - Bundling Policies:
If your business holds other insurance policies (like general liability or workers’ compensation) with the same insurer, bundling these can lead to additional savings. - Payment Options:
Choosing annual or semi-annual payments versus monthly installments might affect premium costs due to financing fees or discounts.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Business Auto Insurance
While securing business auto insurance is vital, many businesses make errors that could leave them vulnerable to financial loss or regulatory penalties. Avoiding these common mistakes will help ensure your insurance coverage is adequate and effective.
Underinsuring Vehicles or Opting for Minimum Coverage
Many businesses try to cut costs by choosing the minimum state-required coverage or underinsuring their vehicles. This can be a costly mistake because if your coverage limits are too low, your business will be responsible for any damages or medical expenses beyond those limits. This can result in out-of-pocket expenses, lawsuits, or bankruptcy in severe cases.
Tip: Assess your business risks realistically and select coverage limits that reflect the potential costs you might face, especially if your vehicles transport valuable goods or carry passengers.
Neglecting to Update Insurance After Adding Vehicles or Changing Business Operations
Business operations evolve. Companies may add new vehicles, change delivery routes, or expand services, but often forget to update their insurance policies accordingly. Failure to notify your insurer about changes can lead to denied claims or gaps in coverage.
Tip: Always inform your insurance provider immediately when you add or retire vehicles, hire new drivers, or change the nature of your business use.
Overlooking Coverage for Hired and Non-Owned Vehicles
Many businesses assume their insurance covers rented vehicles or employee-owned cars used for work purposes, but this is often not the case. Without hired and non-owned auto coverage, your business may be liable for accidents involving these vehicles.
Tip: Make sure your policy includes hired and non-owned auto coverage to protect against liabilities arising from vehicles not owned by your company but used for business activities.
Ignoring Employee Driving Records When Assessing Risk
Your employees’ driving behavior directly impacts your insurance risk and premiums. Ignoring driving records or failing to implement driver safety programs can lead to more accidents and higher costs.
Tip: Conduct thorough background checks on employees who will drive company vehicles and provide regular driver safety training to reduce accident risks and potentially lower insurance premiums.
The Role of Technology in Business Auto Insurance
Technological advancements are revolutionizing business auto insurance by improving risk assessment, enhancing safety, and streamlining claims processing.
Telematics and Usage-Based Insurance (UBI)
Telematics devices installed in vehicles monitor driving behavior, including speed, braking patterns, mileage, and idle time. This data allows insurers to offer Usage-Based Insurance (UBI), where premiums are personalized based on actual driving habits.
Benefits:
- Rewards safe drivers with lower premiums
- Encourages better driving behavior
- Provides real-time feedback to drivers and fleet managers
AI-Powered Claims Processing
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming how insurers handle claims. AI can automate damage assessments, detect fraud, and speed up claims approvals, leading to faster settlements and reduced administrative costs.
Benefits:
- Faster claims resolution
- Improved accuracy and fraud detection
- Enhanced customer experience
Connected Vehicles: New Risks and Opportunities
Connected vehicles communicate with other devices and infrastructure, providing valuable data on vehicle health, location, and driving conditions. While this presents new risks related to cybersecurity and data privacy, it also offers opportunities for more tailored insurance products and proactive risk management.
Implications for Insurers:
- Need for advanced cybersecurity measures
- Opportunities to offer preventive maintenance programs and usage-based policies
Case Study: How Proper Business Auto Insurance Saved a Company
Consider the case of Swift Delivery Services, a mid-sized logistics company operating a fleet of delivery vans. One of their vans was involved in a severe accident that resulted in injuries to the driver and a pedestrian, as well as significant vehicle damage.
Thanks to their comprehensive business auto insurance, Swift Delivery Services was able to:
- Cover all medical expenses for the injured parties
- Pay for vehicle repairs and replacement
- Handle liability claims from third parties without financial strain
Because the company had invested in sufficient liability and physical damage coverage, the accident did not threaten their financial health or business continuity. Swift Delivery Services also benefited from telematics-based discounts due to their commitment to driver safety programs.
Lesson: Adequate business auto insurance can protect your company from catastrophic financial losses and help you maintain operations even after serious incidents.
Also Read : How to network effectively during your MBA program
Conclusion
Choosing the right business auto insurance is vital to safeguard your company’s assets and future. With the wide range of coverage options and modern technologies available, businesses can tailor insurance policies to their unique needs and risk profiles. Regularly reviewing your insurance and staying proactive can prevent costly surprises and help maintain operational continuity.
FAQs
Q1: What is the difference between commercial auto insurance and personal auto insurance?
A1: Commercial auto insurance is designed specifically for vehicles used in business operations. It offers broader coverage, higher liability limits, and protection tailored to the risks businesses face. Personal auto insurance covers private vehicles used for personal activities and typically excludes coverage for business use, which means claims related to business driving can be denied under a personal policy.
Q2: Are all business vehicles required to have commercial auto insurance?
A2: Generally, yes. Any vehicle used primarily for business purposes—such as company cars, delivery vans, or trucks—should have commercial auto insurance. This ensures that your business is protected against liability, property damage, and other risks that arise during commercial vehicle use.
Q3: How does liability coverage work in business auto insurance?
A3: Liability coverage protects your business if your vehicle causes bodily injury or property damage to others. It pays for medical expenses, repair costs, lost wages, and legal fees if your business is held responsible for an accident. This coverage is essential to safeguard your company’s financial health from potentially costly lawsuits.
Q4: What is hired and non-owned auto coverage?
A4: Hired and non-owned auto coverage protects your business when employees use rental cars or their personal vehicles for work-related tasks. This coverage can pay for liability and, in some cases, physical damage, helping protect your company from claims related to vehicles not owned by the business but used for business purposes.
Q5: Can I bundle business auto insurance with other commercial policies?
A5: Yes. Many insurers offer package policies or commercial multi-peril policies that combine business auto insurance with general liability, property insurance, or workers’ compensation. Bundling can simplify management and often results in premium discounts.
Q6: How do telematics and driver monitoring affect my insurance premiums?
A6: Telematics devices collect data on driver behaviors such as speed, braking, and mileage. Insurers use this data to assess risk more accurately and offer usage-based insurance premiums. Safe driving behaviors can lead to lower premiums and incentivize better fleet safety practices.
Q7: What should I do after adding new vehicles to my fleet?
A7: It’s critical to notify your insurance provider immediately whenever you add new vehicles. This ensures your policy is updated to cover all vehicles, preventing coverage gaps that could leave your business vulnerable to uninsured losses or denied claims.

